Different types of cardiomyopathies
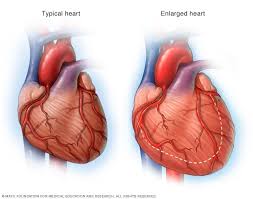
According to experts like Best Cardiologist in Lahore, cardiomyopathies are diseases of the heart muscle that make pumping of blood harder. With progressive disease, the heart weakens further and is unable to pump blood to the body. Read on to know more about cardiomyopathy, its types, symptoms and causes:
Table of Contents
What are cardiomyopathies?
As the name implies, cardiomyopathies refer to diseases of the heart muscle, either due to stiffening, widening or thickening, that make it unable for sufficient blood to be pumped to the body. When the stroke volume becomes minimal with progression of disease, heart failure ensues. Depending on the symptoms and seriousness of disease, this condition is treated with medication, surgery or heart transplant.
What are the symptoms of cardiomyopathies?
In the early stages of disease, cardiomyopathy may present with no symptoms. With the advancement of condition, the following symptoms may appear:
- Difficulty in lying flat
- Breathlessness
- Cough with sputum
- Fatigue
- Irregular heart beats
- Dizziness and fainting spells
- Swelling in the dependent regions like legs and feet
- Chest discomfort
- Abdominal bloating due to fluid buildup
What are the types of cardiomyopathies?
The types of cardiomyopathies include:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: in this type of cardiomyopathy, there is abnormal thickening of the heart muscle. The thickened heart muscle cannot pump blood efficiently, especially since the left ventricle is affected. While this condition can develop at any age, it is mostly hereditary.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy: contrary to hypertrophic heart muscle, this type of cardiomyopathy involves dilation or widening of the left ventricle. Consequently, the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently from the left chamber to the body. This type of cardiomyopathy can occur at any age, particularly secondary to coronary artery disease (CAD), but can also occur due to genetic changes.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy: if the heart muscle becomes stiff, it cannot expand for the filling phase between beats. Therefore, less amount of blood is pumped from the heart to the body. This type of cardiomyopathy is mostly seen in the elderly population.
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia: this is a rare type of cardiomyopathy, with scarring of the right ventricle, leading to rhythm changes in the heart. These changes are mostly due to genetic causes.
- Unclassified: all other types of cardiomyopathies fall in the unclassified category.
What are the causes of cardiomyopathies?
In case of acquired cardiomyopathy, the causes are:
- Metabolic disorders: like chronic diabetes, thyroid disease and obesity
- Valvular diseases of the heart
- Tissue damage secondary to heart attack
- Lack of vitamin B-1 in the diet
- COVID-19 infection
- Inflammatory diseases of the heart
- Long term uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Complications of pregnancy
- Connective tissue diseases
- Hemochromatosis or buildup of iron in the body
- Amyloid proteins in the body (amyloidosis)
- Drugs of abuse like cocaine and amphetamines
- Chemotherapeutic drugs
What are the complications of cardiomyopathies?
Without timely management, cardiomyopathies can lead to the following complications:
- Heart failure: if the heart is unable to meet the pumping needs of the body, heart failure ensues. This life-threatening condition affects other organs as well, and can be fatal without proper management.
- Heart valve problems: with enlargement and stiffening of the heart, as seen with cardiomyopathies, the valves are unable to close properly. This causes valvular insufficiency and results in backflow of blood.
- Clot (Emboli) formation: myopathies combined with valvular insufficiency lead to stasis of blood and clot formation. These clots can travel to the other organs like the brain and impede blood flow to cause strokes.
- Sudden death due to Cardiac arrest: another consequence of cardiomyopathies is irregular heart rhythms that can even cause heart to stop causing sudden death.
How to prevent complications of cardiomyopathy?
The complications of cardiomyopathy can be prevented with heart-healthy lifestyle options, such as:
- Exercising regularly
- Losing weight
- Getting treatment for chronic conditions like thyroid disease
- Getting sufficient sleep
- Avoiding drugs of abuse like cocaine
- Avoiding excessive alcohol
- Eating heart healthy foods
- Reducing stress with meditation
- Getting regular checkups from cardiologists available for consultation at oladoc.com.




